The Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Integrated Education for Disabled Children was introduced in 1992 with a view to providing educational opportunities for children with disabilities in general schools (elementary), to facilitate their retention in the school system. It provided books & stationery, uniform allowance, transport allowance, reader allowance, escort allowance, hostel accommodation and actual cost for equipment. At the initial stage, the scheme is taken up by SCERT, Mizoram. This scheme was implemented both by SCERT and SSA after the introduction of Sharva Shiksha Abbhiyan (SSA) in 2001. In 2009 the scheme for Inclusive Education for Disabled at Secondary Stage was introduced. This scheme aimed at enabling all students with disabilities completing eight years of elementary schooling an opportunity to complete four years of secondary schooling (Class IX-XII). At the initial stage, the scheme is taken up by SCERT, Mizoram and has been implemented under SCERT till 2012. By the year 2013, the scheme was subsumed to RMSA, Mizoram. Inclusive Education Scheme (Elementary & Secondary) is now come under Samagra Shiksha, Mizoram.
Inclusive Education is a new approach of educating all learners irrespective of their strength and weaknesses under the normal school settings. Under Samagra Shiksha, Inclusive Education (I.E) has solely covered differently Abled students enrolled in Government, Government aided and Local Body schools from class –I to Class XII (age between 6 year to 18 years). There are 3158 CWSN students at Elementary and 1410 CWSN students at Secondary Schools. They are provided Aids and appliances, learning materials and other allowances to stimulate effective and for promoting learning environment in school and accelerating retention rate as per approval of Project Approval Board (PAB).
Target Group : The scheme will cover all children from pre School to senior secondary stage studying in Government, local bldy and Government Aided Schools, with one or more disabilities as defined under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act (2016) namely:
- Blindness
- Low Vision
- Leprosy Cured persons
- Hearing Impairment (Deaf & hard of hearing)
- Locomotor Disability
- Dwarfism
- Intellectual Disability
- Mental Illness
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Cerebral Palsy
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Chronic Neurological conditions
- Specific Learning Disability
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Speech and Language disability
- Thalassemia
- Hemophilia
- Sickle Cell disease
- Multiple Disabilities including deaf blindness
- Acid Attack victim
- Parkinson’s disease.
Overview of the programme with focus on its vision, goals and objectives:
The scheme of IE is envisaged to enable all children and young persons with disabilities to have access to secondary education and to improve their enrollment, retention and achievement in the general education system. Under the scheme, every school is proposed to be made disabled friendly.
The scheme aims to enable all students with disabilities completing eight years of elementary schooling an opportunity to complete four years of secondary schooling in an inclusive and enabling environment. Educational opportunities and facilities support the training of general school teachers to meet the needs of children with disabilities.
The scheme will ensure that all children will be identified, aids and appliances and learning materials will be provided. Any architectural barriers will be removed so that the student with disabilities will have access to classrooms, laboratories, libraries and toilets in the school. All general teachers at the secondary level will be provided basic training in special education.
Approach and strategy relating to barrier free access, inclusion, quality improvement, equity.
The students with disabilities need to have access to each part of the school building, no matter what type of aids and appliances he/she is using. This involves removal of physical barriers by means of constructing ramps, railings, special toilets, etc.
Secondly, a child with disability needs to be accepted by every other students and teachers. The school needs to be an inclusive school, and admission is not to be denied to any student regardless of background, race, disability, or any other. The school should welcome each child, and should provide equal opportunities for every child. The school should be sensitive to the special needs of every child and should not discriminate.
Thirdly, all teachers need to be given training to be able to give the essential support to the children with disabilities, and to have the required qualification to teach children with disabilities. Teachers should make sure that seating arrangement, lighting, spacing of seats etc. should suit teach child.
Planning and policies for development of inclusive education in the state.
The Scheme of IEDSS provides facilities to CWSN @ Rs.3,000/- per child under the student-oriented component.
- Braille & Stationery Materials are given to blind or Low vision students who are using braille for their studies.
- Escort Allowances are given to those with Locomotor Impairment, Celebral Palsy and Mentally Retarded who needs another person’s escort, i.e. to physically carried or push in a wheelchair, etc. to go to school. The Escort Allowance is paid to the ‘escort’.
- Reader’s Allowances : Blind or Low Vision students need to engage a Reader, especially from Classes V upwards. Readers are to be paid regular monthly allowances.
- Boarding & Lodging or Hostel Allowances are paid to CWSN who resides in a hostel. In Mizoram, few hostels are run by NGOs as Charity Institutions. The amount provided for Boarding & Lodging is very little and does not meet the requirement. However, it is an incentive for the CWSN as they get their monthly allowance.
- Transport Allowance are paid to CWSN who are living more than 10 kms away from Schools.
- Equipments : CWSN are provided with Aids & Appliances to enable their access to the schools and to aid in their learning in the school. In the Secondary & Higher Secondary Schools, Students with Visual Impairment are the maximum numbers. These students who are neither Blind or Low Vision, but have severe problems with their vision, require Spectacles. It has been learnt that many students who are not able to get spectacles drop out of school. Unfortunately there is no category for these Visually Impaired students under the scheme of IE.
- Blind Students are provided with Braille Slate, Stylus, Brailler, Blind-Stick, Taylor Frame, Abacus, Braille-on(Braille paper), etc.
- Low Vision requires aids like Magnifiers, Large Print Textbooks, etc.
- Hearing Aids are provided to Deaf and Hard of Hearing.
- Children with Locomotor Impairments are provided with artificial limbs, wheelchairs, crutches, and other orthotic aids.
- Children with Mental Retardation needs TLM and learning aids.
- Stipend for girls are given to CWSN girls in through bank account provided by the students.
In addition to the above, CWSN require learning aids and assistive devices depending on their types of disability.
Identification and Assessment:
All children who are suspected of having impairment or disabilities need to be properly identified and assessed. There are two steps in assessment, i.e. Functional Assessment and Medical Assessment.
Functional Assessment can be done in the school by Trained Teachers in the area. This will help in the identification and referral to Medical Specialists.
Next step is Medical Assessment where a thorough medical examination need to be conducted by Medical Specialists namely, E.N.T Specialists, Eye Specialists, Ortho Specialists, Psychiatrists. Some cases require the intervention of Audiology and Speech Pathologists, Clinical Psychologists, Physio Therapists and Occupational Therapists.
During Medical Assessment, the Specialists will prescribe aids & appliances determine the percentage of the disabilities and Disability Certificate may be issued. With this Certificate, Identity Card will be issued. This Identity Card will be used for concessions, reservations and other facilities which persons with disabilities are entitled.
All students with disabilities need to undergo Medical Assessment which will certify them to receive the facilities provided under the scheme.
In the rural areas where there are no Medical Specialist Doctors, Assessment Camps are conducted. Assessment and Certification camps are ongoing programmes in Mizoram initiated by Social Welfare Department in collaboration with Health Department, SCERT, NERC-NIOH and SSA.
ADVOCACY AND STAKEHOLDERS PARTICIPATION
The scheme of IE aims at integrating children with disabilities with the community so that they will enjoy equal benefits and opportunities. The children with disabilities need to be prepared for social integration, to have a normal growth and development, and to face their future with confidence.
Parents and caretakers of the children with disabilities have a very important role to play in the development of the children with disabilities. It is important that they share their achievement and disappointments and that they encourage each other. These parents and caretakers need training and counseling in management of these children.
Also, training of educational administrators, principals and heads of institutions is to be conducted at regular intervals so as to make the education system inclusive. General teachers and special teachers need to be trained thoroughly, as untrained teachers may act as barriers for children with disabilities.
Other programmes implemented :
- Functioning of Resource Rooms: All facilitated 10 Resource Rooms (formal) and 16 BRC’s Resource Rooms are in full function. Children who need screening are sent to these resource rooms for further assessment which has been found to be very useful especially for remote places.
- Environmental Building Programme: Community Sensitization Programme is successfully conducted at 26 Blocks at different districts. The programme is organized with the coordination of SMDC. The programme is found to be fruitful to enhance the acceptance of disabled person in the community. It also helps in establishing disabled friendly environment of the society.
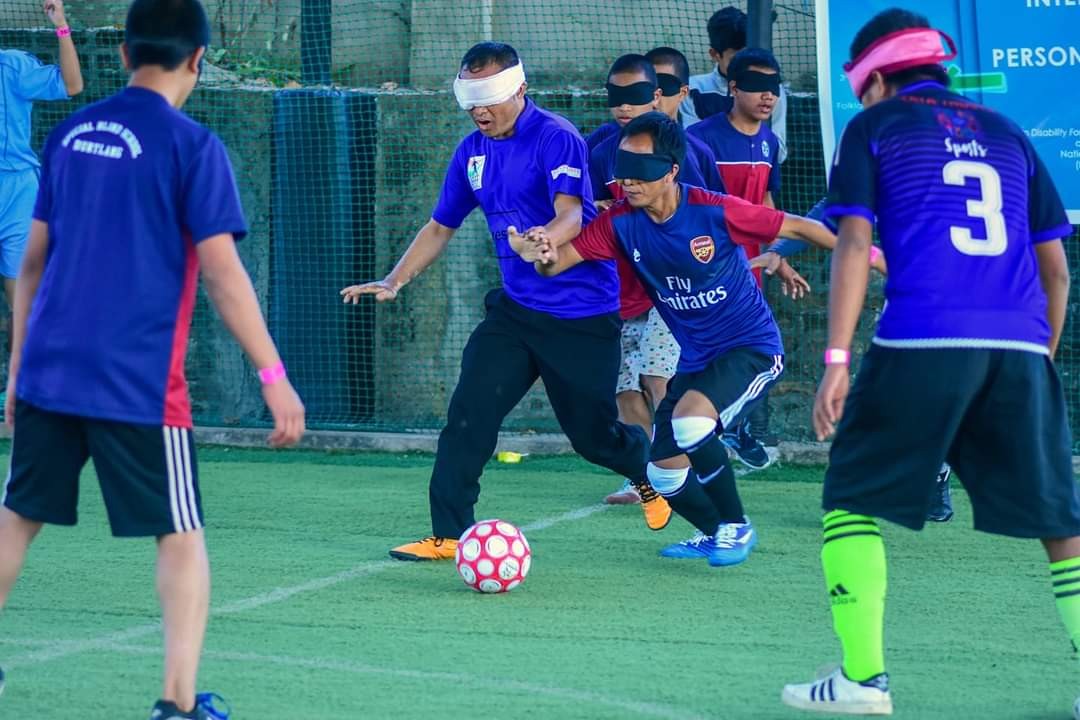
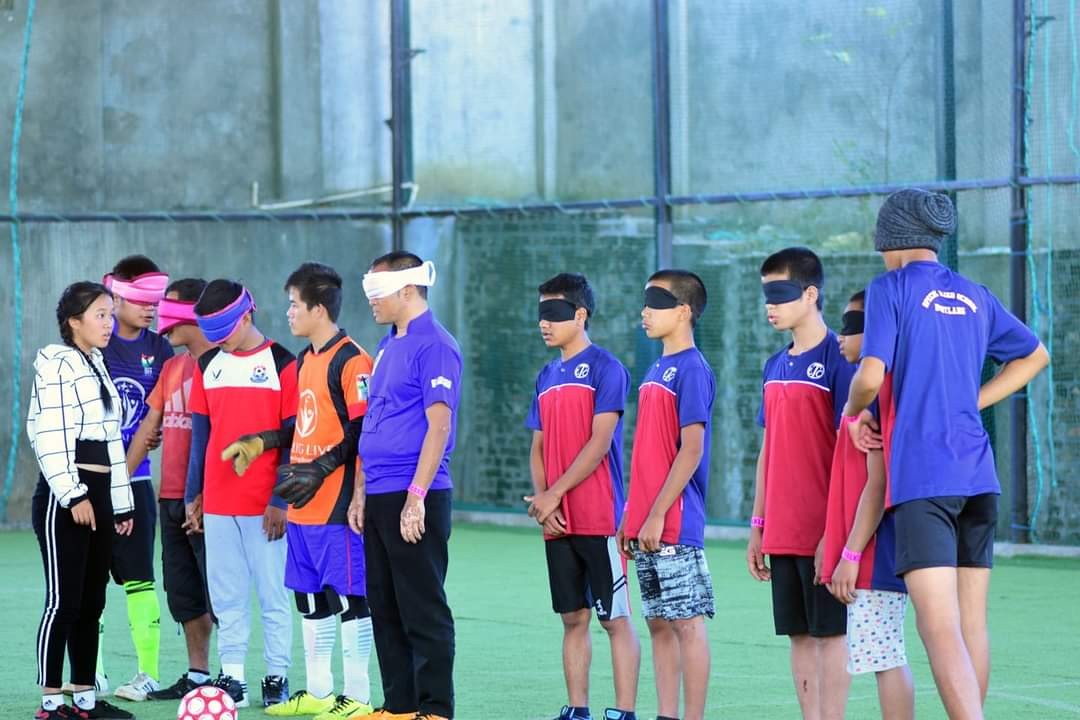
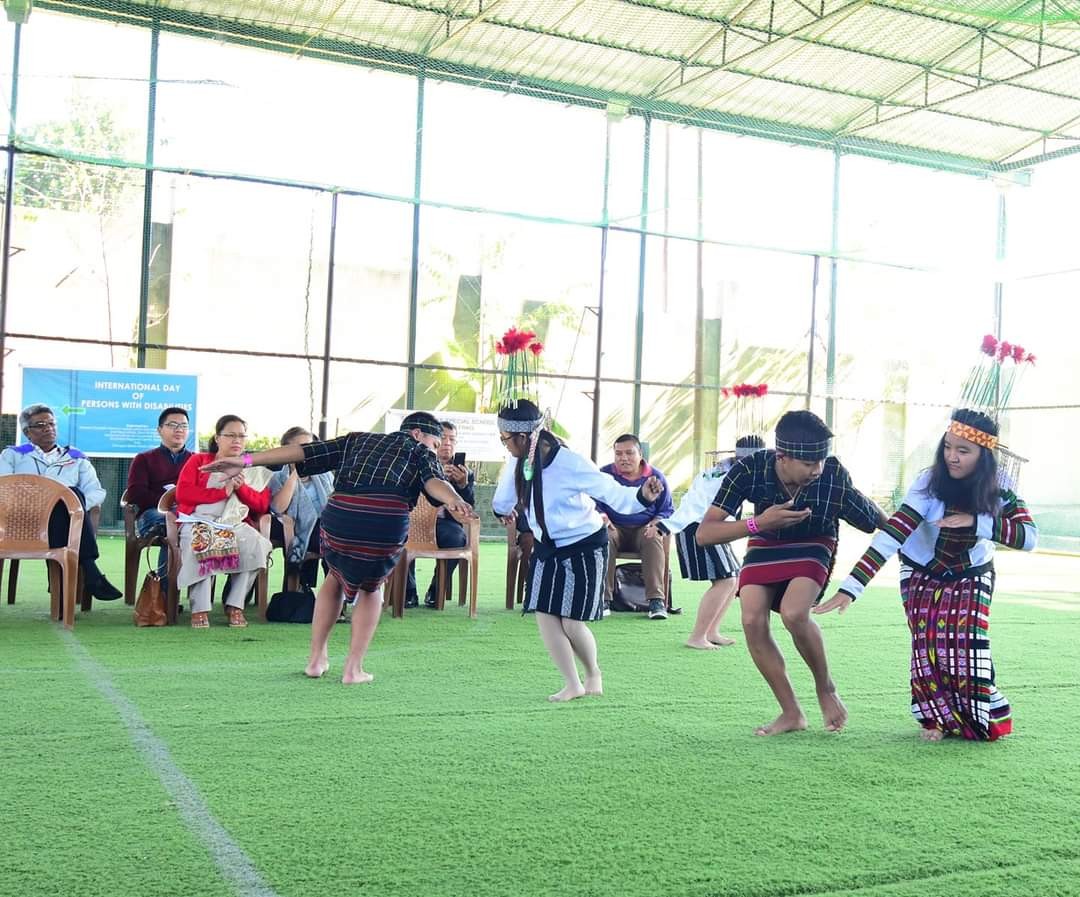
- Special Olympics cum World Disabled Day(with NGO’s/Special Schools): International Day for Persons with Disabilities is observed on 4th December, every year. On this day, all disabled children are participated in each suitable category of items based on areas of disabilities. Cash prize, trophy and medal are given to top 5 winners. The programme is observed in all districts successfully.
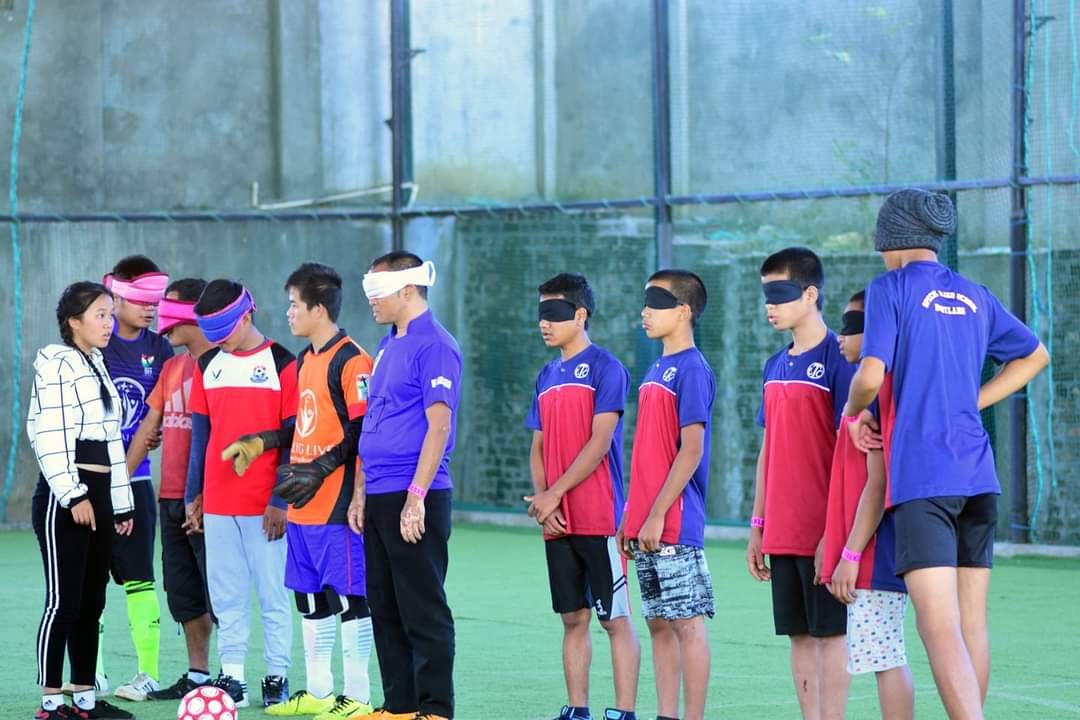
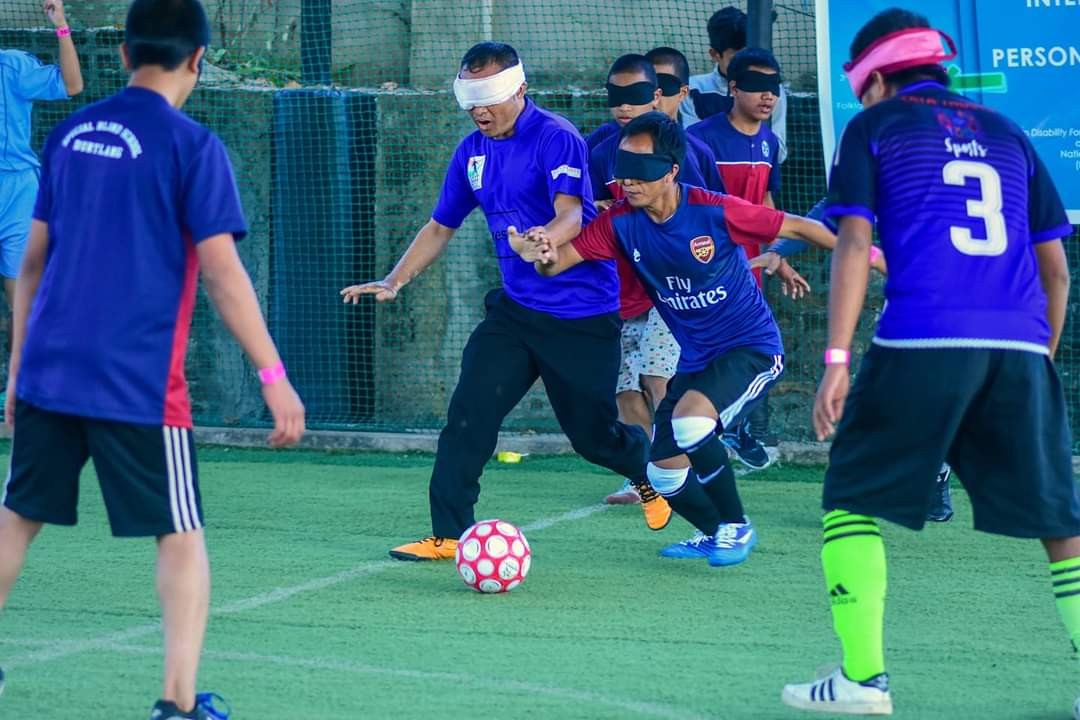


World Disabled Day Celebration: